PFAS in Building Materials
PFAS have many uses in the building industry, including in roofing materials, paints and coatings, sealants, caulks, adhesives, carpets, and more. PFAS provide highly desirable functions such as weatherproofing, corrosion prevention, lubrication, friction reduction, and grease and water resistance. Read the full report here.
Flooring
PFAS have been used extensively as stain, soil, and water repellents in carpets and rugs.
PFAS used:
- Side-chain fluoropolymers
- Propriety fluorochemicals
- Monomeric PFAS
Alternatives:
- Siloxane and silicone polymers
- Paraffins
- Polyurethanes
- Dendrimers
- Acrylics
- Urethanes
Non-Chemical Alternatives:
- Modification of the fiber shape
- Or choosing fiber materials that are inherently resistant to water and oil
Farbics
PFAS are added to furniture fabrics for their stain-, soil-, and water repellent properties in fabrics.
PFAS Used:
PFAS-containing sprays include:
- Teflon
- Nanosphere®
- Scotchgard®
- Capstone®
- Crypton®
- Crypton® Green
- Nanotex®
- Nanotex® + Durablock®
- GreenShield®
Alternatives:
Paraffin or Silicone-based PFAS polymeric spray finishes include:
- AquapelTM
- Crypton® Zero
- NikWax®
- ZelanTM R3
- EcoRepel®
- Altopel F3
- Arkophob®
- Arroshield EVO
- SBI
- Phobotex® WS
Other PFAS alternatives include:
- Nanosilica treatments
- Olefinic-based fibers (polypropylene) treatment
- Textiles with tighter weaves naturally are more water- and oil-resistant
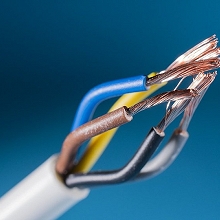
Wire and Cable
The insulating properties of fluoropolymers allow for the use of thinner insulating sheaths that are flexible, durable, and stand up to high temperatures.
PFAS Used:
- PTFE
- ETFE
- ECTFE
- Perfluoro-alkoxy
Trademarked PFAS:
Alternatives:
- Silicone
- Chlorosulfonated polyethylene
- PVC
- Polyethylene
- Cross-linked polyethylene
- Chlorinated polyethylene
- Ethylene vinyl acetate
- Thermoplastic elastomer
- Neoprene
- Ethylene-propylene rubber
- Nylon
Seismic Damping Systems
PFAS are employed in seismic dampers used to make large buildings and bridges resilient to earthquakes.
PFAS Used:
- PTFE
- Other fluoropolymers
Alternatives:
Sealants
Fluorinated sealants are used to create a grease-resistant and water-resistant barrier that protects building materials from stains, mold, and physical damage.
Grout, tile, stone, and concrete sealers
PFAS Used:
- Resin-based fluorocarbons
- PCTFE
- Perfluoroelastomer
- Perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids
- Fluorinated polyurethane dispersions
- Fluorinated acrylic polymers
- Fluoro-acrylate modified urethane emulsions
- Fluorinated acrylic polymers in ethyl acetate
- Fluorochemical acrylic resin concentrate in ethyl acetate
Alternatives:
- Silicones
- Epoxy
- Polyester
- Phenolic
- Urea
- Furane resins
Caulk
PFAS Used:
Alternatives:
- Urethane
- Silicone
- Polysulfide
- Acrylic
O-Rings
PFAS Used:
- Teflon
- Fluoropolymers
- Fluoroelastomers
Alternatives:
- Polyacrylate
- Nitrile
- Other non-fluorinated elastomers
This webpage and report was developed by the Green Science Policy Institute, whose mission is to facilitate responsible use of chemicals to protect human and ecological health.
Information about PFAS and their use in building materials was obtained by searching peer-reviewed literature, government and non-governmental reports, patents, and company websites.
The alternatives mentioned are either readily available and identifiable as suitable alternatives, or listed as such in a report, research article, or patent. Note that some of the materials listed as alternatives contain chemicals of concern other than PFAS.
Read the full report here.